Overview – Project Portfolio Dashboard Templates
- Definition of Project Portfolio Management: An overview of what PPM is and its purpose in aligning projects with organizational strategy.
- Importance of PPM: Briefly discuss how PPM contributes to achieving strategic goals and efficient resource allocation.
Key Components of Project Portfolio Management
- Project Selection and Prioritization: Explain the criteria and processes involved in selecting and prioritizing projects within a portfolio.
- Resource Allocation and Management: Discuss how PPM helps in optimally distributing resources across projects.
- Performance Measurement: Outline how project performance is tracked, including key performance indicators (KPIs) used in PPM.
- Risk Management: Describe the strategies for identifying and mitigating risks in a project portfolio dashboard template.

Benefits of Effective Project Portfolio Management
- Strategic Alignment: Elaborate on how PPM ensures that projects are aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Discuss the role of PPM in providing insights and data for better decision-making.
- Resource Optimization: Explain how PPM leads to efficient use of resources, reducing costs and maximizing value.
- Risk Mitigation: Highlight how PPM helps in foreseeing and mitigating risks.
Challenges in Project Portfolio Management
- Balancing Competing Priorities: Discuss the challenges of managing and prioritizing multiple projects with varying objectives.
- Resource Constraints: Talk about the difficulties in managing limited resources across numerous projects.
- Change Management: Address the challenges in adapting to changes within projects and the portfolio.
Methodologies in Project Portfolio Management
- Agile Portfolio Management: Describe how Agile methodologies are applied in PPM.
- Waterfall Model in PPM: Explain the traditional approach of the Waterfall model in the project portfolio dashboard template.
- Hybrid Approaches: Discuss the integration of different methodologies to suit specific organizational needs.
Agile Portfolio Management (APM) is an approach that applies Agile principles and methodologies at the portfolio level to manage and prioritize projects. It is designed to help organizations quickly adapt to change, deliver value incrementally, and align project outcomes with business strategy. Here’s an in-depth look at Agile Portfolio Management.
Introduction to Agile Portfolio Management
Agile Portfolio Management is a strategic approach that combines Agile practices with traditional portfolio management. It focuses on adaptability, customer-centricity, and delivering value in iterative cycles. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on upfront planning and rigid structures, APM embraces change and promotes flexibility.
Principles of Agile Portfolio Management
- Customer Value: Prioritize projects that provide the most significant value to the customer.
- Iterative Planning: Use iterative cycles to plan and re-evaluate the portfolio continuously.
- Flexible Prioritization: Respond to changes in the market or organization by adjusting priorities as needed.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Empower teams to make decisions quickly and autonomously.
APM vs. Traditional Portfolio Management
Traditional portfolio management often involves long-term planning and a fixed approach, which can lead to a slow response to change. APM, on the other hand, advocates for a more dynamic model, where plans are revisited frequently, and adjustments are made regularly to ensure alignment with business goals and market demands.
Format of the Project Portfolio Dashboard Template

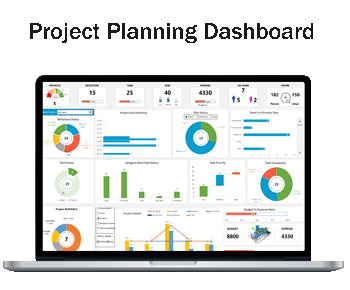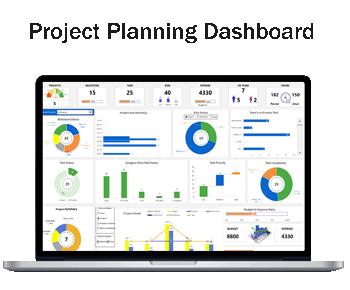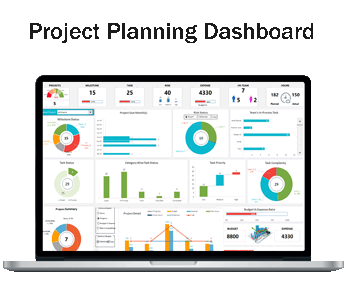
1- Project Tracking at a Glance
- Project Count and Status: The dashboard shows the total number of projects and milestones, alongside their completion status, allowing managers to quickly gauge overall progress.
- Task Overview: Tasks are broken down by status, category, priority, and complexity, providing a detailed view of what’s open, in progress, on hold, or completed.
2- Risk Management and Resource Allocation
- Risk Assessment: The dashboard categorizes risks by their impact on the project or milestone and offers a visual summary of high-, medium–, and low-risk items.
- Expense Tracking: A clear summary of budget versus expenses is displayed, ensuring financial resources are monitored and controlled effectively.
3- Team Performance Metrics
- Human Resources Overview: The dashboard provides insight into the HR team’s involvement, displaying the number of team members and their hours planned versus actual.
- Efficiency Analysis: Task complexity and in-process tasks are visualized, enabling managers to identify areas where the team is excelling or where efficiency gains are possible.
4- Project Milestones and Deadlines
- Milestone Status: A timeline of project milestones, their deadlines, and completion percentages are outlined, helping keep track of critical dates and deliverables.
- Project Due Dates: Upcoming project due months are highlighted to prevent any overdue tasks and keep everything on schedule.
5- Data-Driven Decision-Making
- Graphs and Charts: Various charts, such as pie charts, bar graphs, and histograms, translate data into an easily digestible format.
- Summary Widgets: The dashboard includes widgets that summarize the projects, tasks, risks, and resource allocation, offering quick insights without the need for deep dives into reports.
Milestone Tracking and Status

The dashboard presents a milestone section, where each project phase is broken down with start and end dates, providing a clear timeline. Each phase is represented by donut charts showing the task completion status:
- Completed Tasks: Indicated in green, showing the number of tasks that have been finished.
- Open Tasks: In orange, highlighting tasks that are still in progress.
- Overdue Tasks: In red, signaling tasks that are behind schedule.
This visualization aids project managers in monitoring progress and identifying phases that may require additional attention or resources to meet deadlines.
Task Management Overview
A comprehensive breakdown of tasks is given, categorized by:
- Total Number of Tasks: Demonstrating the workload and scope of the project.
- Risk Assessment: With a count of 51, risks are quantified, allowing for a prioritization of risk mitigation strategies.
- Expense Tracking: The dashboard shows a budget vs. actual expenses comparison, which is critical for financial oversight.
Human Resources Allocation
The HR section reflects the number of team members and compares planned hours against actual hours worked, providing insights into:
- Team Utilization: Understanding whether the human resources are over or under-utilized.
- Efficiency Analysis: Indicating if the project is on track in terms of labor and if any adjustments need to be made.
Task Details
- Priority: Tasks are segmented into high, medium, and low priority, enabling the team to focus on critical areas first.
- Complexity: It provides an understanding of the project’s complexity, with a visual split between low, medium, and high-complexity tasks.
Task Status Graphs
- Pie Charts: Offer a quick visual reference to the proportion of tasks in different priority and complexity categories.
- Bar Graphs: These represent the number of tasks in each status category, offering a quick comparison between open, in-process, on-hold, canceled, and completed tasks.
Risk Management
- Outstanding Risk: A donut chart indicates the number of risks that have been completed versus those that are outstanding. With 51 total risks, 40 are outstanding, representing a significant area that requires attention.
- Risk Status: A bar graph differentiates risks based on their level (high, medium, low), allowing managers to prioritize risk mitigation efforts accordingly.
- Employee Wise Risk Status: This presents a breakdown of risks associated with individual team members, color-coded by risk level, which can guide managers in providing support where needed to mitigate risks effectively.

Project Task Details
- Task List: A table lists tasks, milestones, start and end dates, duration, progress, status, and associated risk levels. This comprehensive view helps in tracking the project’s progress and identifying potential delays or areas of concern.
- Task Progress: Visual progress bars offer a quick glimpse into the status of each task and milestone, highlighting how much of the task is completed.
Expense Tracking
- Expense Overview: The dashboard provides an expense tracker, comparing the budget to actual expenses. This is critical for financial oversight and ensuring the project remains within financial constraints.
Human Resources Allocation
- Team Composition: The HR section displays the number of team members and compares planned hours against actual hours worked, which helps in understanding resource allocation and utilization.
- Efficiency and Productivity: The comparison of planned versus actual hours can indicate efficiency and productivity levels, potentially highlighting areas where process improvements could be made.
Implications for Project Management
Risk Identification and Mitigation
The dashboard enables quick identification of high-risk areas, facilitating proactive management and allocation of resources to address them. This real-time risk assessment is crucial for maintaining project health and meeting deadlines.
Project Tracking and Coordination
It provides a snapshot of project tasks and milestones, enabling project managers and team members to coordinate efforts effectively. Managers can use this information to adjust timelines, re-prioritize tasks, and communicate changes to the team and stakeholders.
Financial Management
With the expense tracking provided, managers can make informed decisions to avoid cost overruns. The visual representation of budget versus expenses allows for quick assessments and adjustments as needed.
Resource Management
Understanding how team members are associated with different risk levels can lead to better support and training, ensuring that risks are managed effectively. The HR data also aids in balancing workloads and ensuring that team members are neither overworked nor underutilized.
Task Management Section

- Task Status: A donut chart visualizes the proportion of tasks that are open, in process, or closed, which is essential for tracking progress and ensuring timely task completion.
- Category Wise Task Status: A bar chart breaks down tasks into categories, helping managers to understand the distribution of work and identify areas that may require more attention.
- Task Priority: This donut chart segments tasks by priority level (low, medium, high), aiding in prioritization and resource allocation.
- Task Complexity: Another donut chart categorizes tasks by complexity, which is crucial for resource planning and identifying potential bottlenecks.
Detailed Task Information
- Task List: A table provides detailed information about specific tasks, including type, description, start and end dates, progress, and status. This information is valuable for micromanaging project details and keeping tasks on track.
- Progress Bars: Visual bars represent the completion percentage of tasks, offering a clear indication of progress and highlighting any delays.
- Project Task Summary: A histogram shows the number of tasks in each status category, which is useful for assessing the overall project health and operational efficiency.
Implications for Project Management
The dashboard serves as a strategic tool for project managers by:
- Enhancing visibility into project performance and identifying areas that require immediate action.
- Enabling informed decision-making through a comprehensive view of project metrics.
- Assisting in workload management and efficient resource allocation.
- Providing a platform for continuous monitoring and improvement of project tasks and milestones.
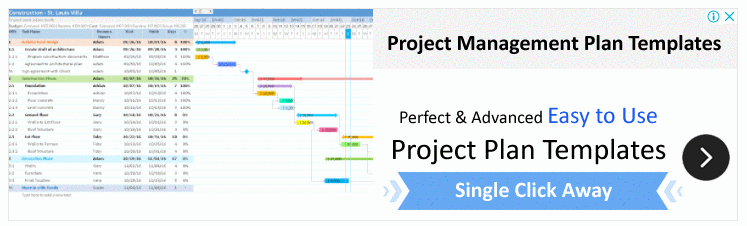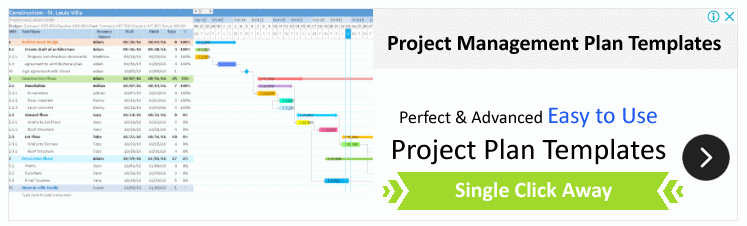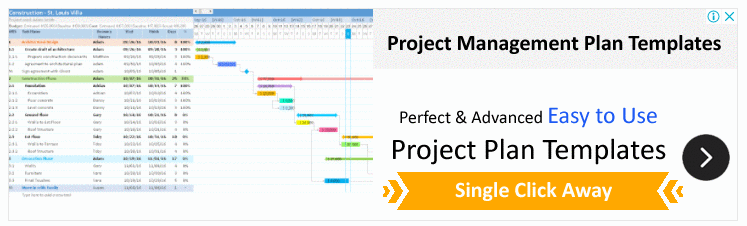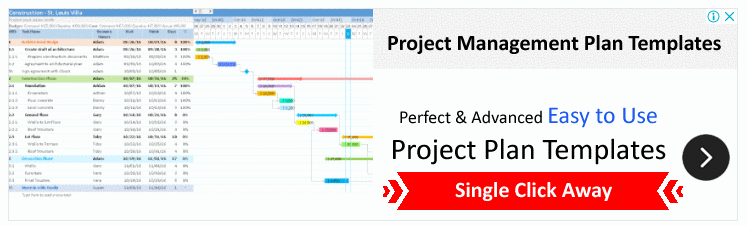
Gantt Chart Dashboard

Project and Task Tracking
- The left side of the dashboard lists projects, milestones, and tasks in a structured hierarchy. This section seems to include details such as the type of entry (project, milestone, or task), the percentage of progress, start dates, and end dates.
- Projects, milestones, and tasks are color-coded, likely indicating their status (e.g., completed, in-process, overdue).
- There is a filter option to view entries based on their status-completed, in-process, or all.
Timeline Visualization
- The Gantt Chart spans across the right side of the dashboard, providing a visual timeline of the projects and tasks.
- Each bar on the Gantt Chart represents a task or a project with its respective duration from the start date to the end date.
- Overdue tasks or milestones might be highlighted in red, giving immediate visual cues of delays or issues that need attention.
Functionality and Navigation
- The top of the dashboard has various tabs and buttons that suggest functionalities such as exporting data, filtering content, and navigating to different views like Calendar, To-Do List, Reports, and Contacts.
- The dashboard seems to have interactive elements, possibly allowing users to click on tasks or milestones to get more details or to update their status.
Benefits of Using a Gantt Chart in Project Management
Planning and Scheduling
- Gantt Charts help in planning out the timeline for each task and milestone, ensuring a clear path to project completion.
- They provide a visual timeline for the project, allowing project managers to identify the sequence of tasks and the dependencies between them.
Resource Management
- By laying out the tasks across a timeline, project managers can better allocate resources and ensure that team members are not overburdened.
- It can also highlight when resources may be under-utilized, allowing for adjustments to be made.
Progress Monitoring
- Progress bars indicate how much of the task has been completed, giving an instant view of the project’s advancement.
- Managers can quickly spot which tasks are on track and which are lagging, facilitating swift action to address any issues.
Communication and Transparency
- Gantt Charts serve as an excellent communication tool, providing team members and stakeholders with a clear understanding of project timelines and expectations.
- They promote transparency in the project’s progress and can be a focal point in project meetings and discussions.
Conclusion: Benefits of Utilizing a Dashboard
Strategic Project Alignment
A dashboard such as the one visualized ensures that all projects align with the strategic objectives of the organization. By offering a centralized view of project health, managers can make informed decisions that steer the project portfolio dashboard template toward the desired outcome.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
With a shared dashboard, teams can communicate more effectively. The visual nature of the dashboard ensures that every team member understands the project’s status, goals, and their role in achieving them.
Proactive Issue Resolution
The dashboard enables project managers to identify potential issues before they escalate. With real-time data, managers can deploy resources to where they are needed most, ensuring project agility and resilience.
Efficient Resource Management
One of the key advantages of a project portfolio dashboard template is its ability to display resource allocation across all projects. Managers can optimize their teams’ workload, prevent burnout, and ensure that every project has the necessary resources to succeed.